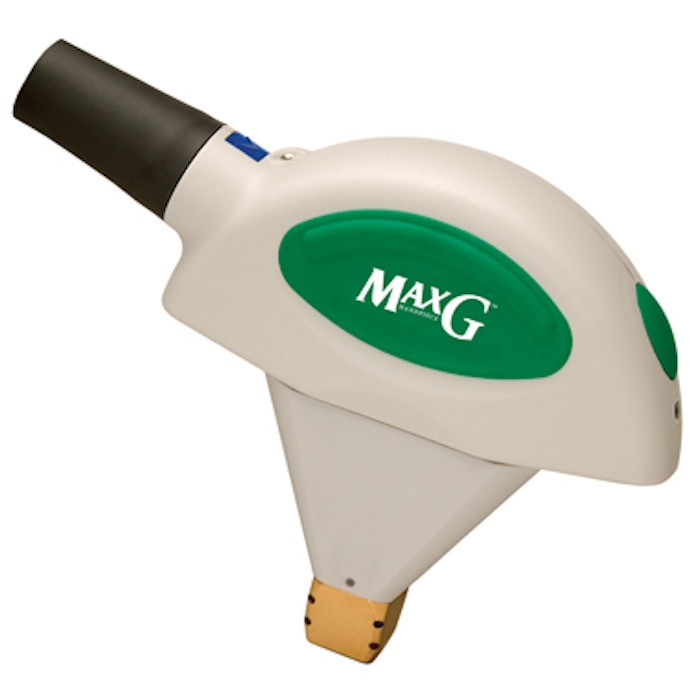
A new study, published in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology (November 2017), found that pulsed dye lasers (PDL) and the MaxG Optimized Light Handpiece (500-670nm and 870-1200nm) offer the best outcomes for patients with facial telangiectasia. Lin Gao, MD, et al, of the Xijing Hospital department of dermatology in Xi’an, China, performed a retrospective analysis of 416 patients with facial telangiectasia who were treated by PDL or IPLs in their department from August 2012 to March 2015.
Each subject had received one of the following five treatments (two sessions at 6-week intervals): PDL (595nm, 9-12 J/cm2), MaxG (500-670nm and 870-1200nm, 30-46 J/cm2), IPL (560-1200nm, 18-24 J/cm2), M22 560 (560-1200nm, 15-18 J/cm2) or M22 590 (590-1200nm, 15-20 J/cm2). Two non-treating physicians graded results following the final treatment.
Ninety-five percent of patients treated with PDL or the MaxG had marked improvements or nearly complete clearance of the lesions, compared to 41.38%-56.58% of patients in the other three groups. The authors concluded that both PDL and MaxG treatments resulted in significantly superior vessel clearance than the IPL systems with other wavelength bands and relatively lower fluences, and that the fluence levels accounted for the differences in efficacy between the various IPL systems.
Image MaxG handpiece.