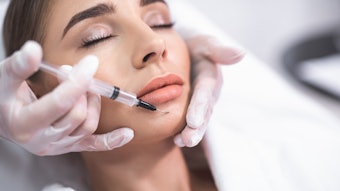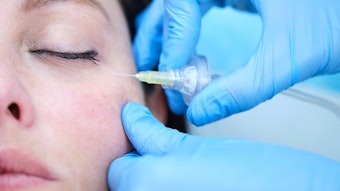
Combining hyaluronic acid fillers, botulinum toxin injections and lash treatments as part of facial rejuvenation treatments leads to significant improvement in appearance, self-confidence and feelings of well-being, according to the outcomes of a four-month study published in the Aesthetic Surgery Journal (February 2022).
Related: Combination Toxin and Filler Treatment Boosts Patient Retention
Joel L Cohen, MD, et al, evaluated the impact of multimodal facial aesthetic treatment on self-reported psychological and social outcomes through a prospective, multicenter, four-month study that included 100 subjects (35 to 65 years of age).
Related: Multi-modal Laser Treatments Safe and Effective
Subjects received combined treatment with: onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox Cosmetic) for treatment of dynamic rhytids; HA dermal fillers VYC-20L (Juvéderm Voluma XC) for volume restoration and HYC-24L (Juvéderm Ultra XC) and/or HYC-24L+ (Juvéderm Ultra Plus XC) for lines and folds; and bimatoprost ophthalmic solution 0.03% (Latisse) for treatment of eyelash hypotrichosis.
The fillers were injected on Day 1, with touch-ups performed on Day 14. OnabotulinumtoxinA was injected at month 3 into glabellar lines and/or crow’s feet lines. Patients applied bimatoprost to eyelashes once daily for 17 weeks.
Related: The Latest on Botulinum Toxin Dosage and Indications
The outcomes that were assessed included: mean change from baseline on FACE-Q Psychological Well-being and Social Confidence Scales; FACE-Q Aging Appearance Appraisal Scale; and FACE-Q Age Appraisal Visual Analog Scale.
Of 100 patients treated, 93 were evaluated four months posttreatment. Significant improvement from baseline was observed on the FACE-Q Scales for Psychological Well-being (mean change, −19.9), Social Confidence (mean change, −18.2) and Aging Appearance (mean change, −28.5). Subjects’ self-assessed age was, on average, 0.1 years older than actual age at baseline and 4.5 years younger at month four.
Related: Tips To Reduce Bruising After Filler Treatments
Forty-two subjects experienced adverse events, all mild to moderate. Of the 91 procedure-related AEs, the most common were bruising (61 events), injection site pain (12 events), injection site redness (8 events) and swelling (7 events). The number of patients who experienced a treatment-related AE attributable to one of the study products was 4/100 (4%) for bimatoprost, 12/96 (13%) for VYC-20L, 16/80 (20%) for HYC-24L, 15/78 (19%) for HYC-24L+ and 2/96 (2%) for onabotulinumtoxinA.