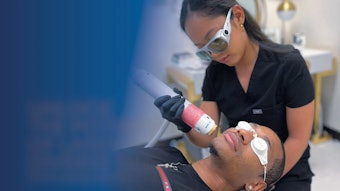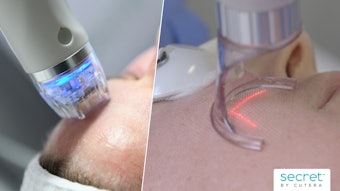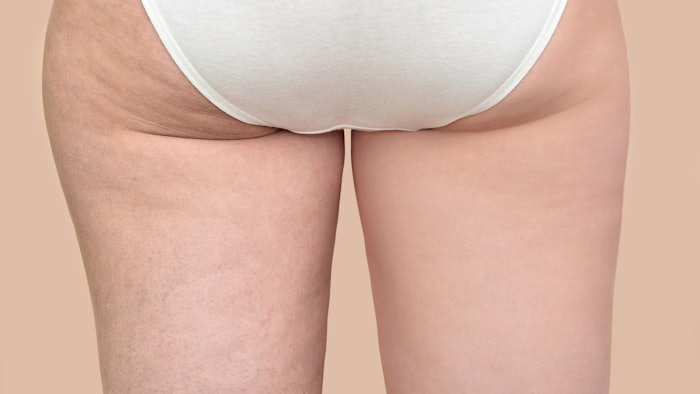
Researchers set out to evaluate a noninvasive approach to improving both cellulite and skin laxity through the use of rapid acoustic pulse technology (Soliton, Allergan Aesthetics), which cause acoustic subcision. The study measured safety, efficacy, tolerability and participant satisfaction, and showed that a single treatment session with the device can provide meaningful improvement in the appearance of cellulite and skin laxity.
These findings were published in the Journal of Lasers in Surgery and Medicine (January 2022).
Related: Combination Contouring Treatments
Women (n = 56) with moderate to severe cellulite underwent a single Soliton treatment session without anesthesia. The investigators selected cellulite either on the right or left side buttock/leg area with the most or more serious cellulite; they marked 9-15 treatment areas (i.e., depressions, dimples, ridges, etc.). One to two one-minute acoustic subcision doses were administered at a pulse rate of 50 Hz to each treatment area. The total number of treatment doses was determined by the number of identified treatment areas.
At baseline and 12-week post-treatment timepoints clinical photographs were collected. At the 12-week post-treatment mark cellulite outcomes were also assessed using a 6-point simplified Cellulite Severity Scale (CSS), Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale (GAIS) and a participant satisfaction questionnaire. Laxity improvement was measured using a 4-point Laxity Score (LS) and GAIS.
Related: Ultrasound Useful in Guiding Cellulite Treatments
Participants had a mean CSS reduction of 1.01 (a 29.5% reduction from baseline) at 12 weeks. Cellulite was graded as improved, much improved or very much improved using the GAIS at 90.9% of treated locations, and all participants reported positive satisfaction responses. Post-treatment photographs were evaluated and correctly identified by blinded independent reviewers for 96.4% of participants.
Related: Combination HIFEM with RF and Targeted Pressure Improves Body Contour
There was a mean LS reduction of 0.57 (27.9% reduction from baseline). GAIS for laxity was graded as improved, much improved or very much improved in 67.3% of treated areas. There were no unexpected or serious adverse events noted at the time of the treatment or the follow-up. The overall average pain score during the treatment was a 2.4 on a 0-10 pain scale, and it was 0.3 immediately post treatment.