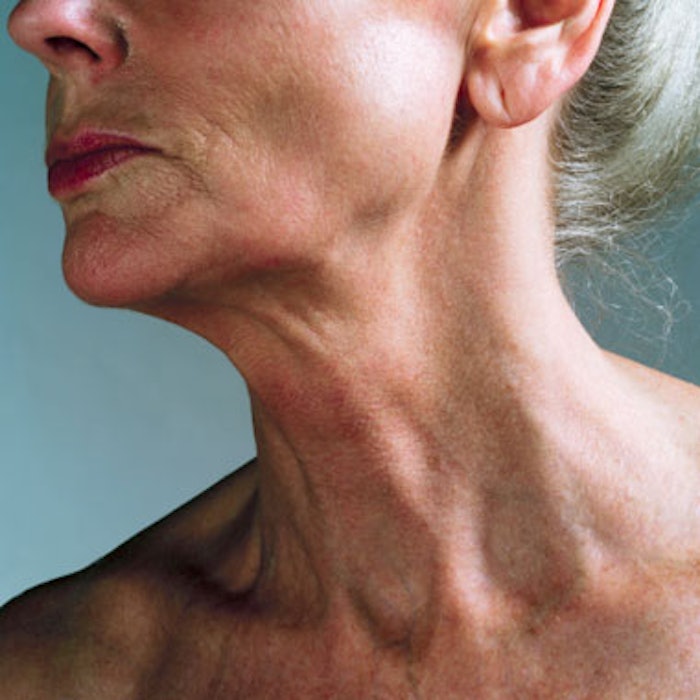
A recent literature review of botulinum toxin treatment for mild-to-moderate platysma bands by Jack L. Kelly, MD, et al, found the treatment to be both safe and effective and offered injection technique guidelines for optimal outcomes.
Published in the February issue of the Aesthetic Surgery Journal, the review included studies culled from three electronic databases—Ovid MEDLINE, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library—between January 1985 and December 2017. Three studies met the inclusion criteria, with a total of 78 subjects. Incobotulinumtoxin A (Xeomin, Merz) was used in 62.3 percent (n = 45/78) of patients; 38.4 percent (n = 30/78) received abobotulinumtoxin A (Dysport, Ipsen).
Two weeks following treatment, the studies showed a mean score improvement of 2.0 points and a response rate of 93.7 percent. At three months, the mean score improvement was 1.2 points with a response rate of 86 percent. All three studies used a standard injection technique of intramuscular injections spaced 1cm to 2cm apart into the most prominent part of the band with a range of two to six injections per band. The maximum dose per band was 20 IU incobotulinumtoxin A and 5 IU abobotulinumtoxin A.
There was a total complication rate of 15.4 percent (12 subjects), which included ecchymosis/hematoma (8.9 percent, 7 patients), mild dysphagia (5.2. percent, 4 patients) and neck weakness (1.3 percent, 1 patient).
The authors note that achieving safe and effective outcomes requires knowledge of botulinum toxin dosages and proper injection technique involving multiple incremental intramuscular injections into the most prominent part of the band.
Image copyright Getty Images