In the evaluation of the effects of a series of laser treatments with very short, nanosecond pulses in the treatment of melasma on Caucasian women, researchers discovered that low-fluence 1,064 nm QSNY laser effectively provides long-term results in melasma treatment. Their findings were published in the Journal of Lasers in Surgery and Medicine (September 2021).
Related: Melasma Diagnosis and Management: An Evidence-Based Approach
The study included 40 polish women with Fitzpatrick skin phototype II-III and melasma. Subjects received nine treatments with 1,064 nm Q-switched neodymium:yttrium-aluminum-garnet (QSNY) laser (pulse with 5 ns; spot size, 6-8 mm; fluence, 1.7-3.2J/cm2; 2-8 passes). The researchers evaluated the melanin index (MI) and erythema index (EI) using the Mexameter MX18 and the modified Melasma Area Severity Index (mMASI). The participants also self-assessed their treatment results, and 21 subjects returned for a 12 month follow-up.
Related: Synbiotic Supplementation Reduces Severity of Melasma
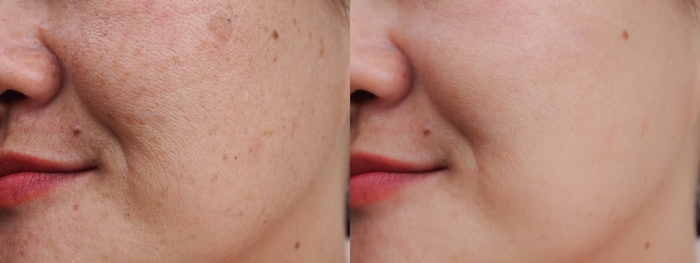
The mean MI and mMASI scores showed significant improvement and reduction in melasma pigementation. EI reduction was also achieved. Of the participants, 70% rated the laser as a method that met their expectations for treating melasma. The one-year follow up showed that the reduced melasma effect was maintained, and patients also noted improvement in skin radiance, smoothness, brightness, hydration and regeneration.
Related: Tranexamic Acid vs. Vitamin C with Microneedling for Melasma
With these results and no adverse effects being observed, researchers deemed low-fluence 1,064 nm QSNY laser as an effective, safe and noninvasive method for long-term melasma treatment results.